Yesterday we released a massive new dataset comprised of all 95,000 mentions of climate change on television news on CNN, MSNBC and Fox News 2009-2020 and BBC News London 2017-2020. Each mention includes the precise date and time of the mention, the station and show it appeared on, the words spoken in the 15 second clip containing the mention and a URL out to the Internet Archive's Television News Archive to view the full one minute clip containing the mention.
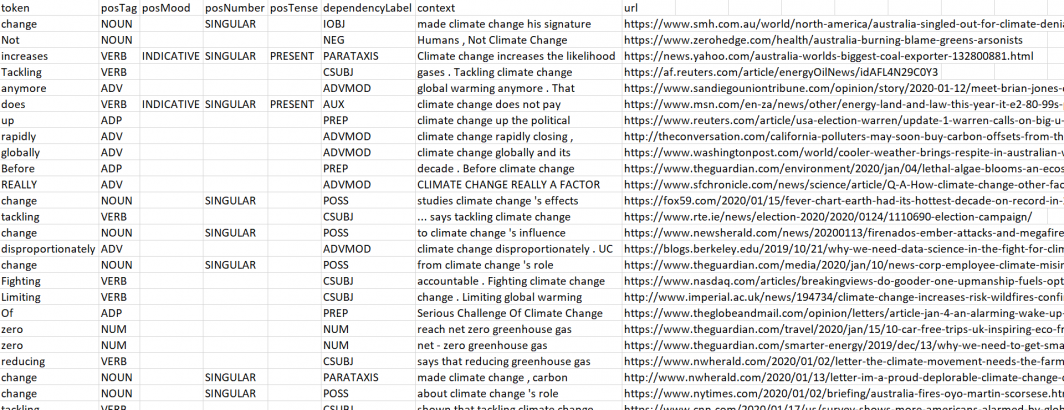
To complement this rich new dataset, we are releasing a second, even more powerful dataset, of 6,092,147 linguistically annotated 5-word snippets of climate change mentions, drawn from our 101-billion-word Web Part Of Speech dataset. The Web Part of Speech dataset is organized by token/context/minute, in which the system aggregates all coverage monitored by GDELT each 15 minutes (now each minute) and runs a random sample of around 100,000 articles a day through Google's Cloud Natural Language API. It then compiles all of the coverage in the given interval (15 minutes from 2016 – Jan. 17, 2020 and every minute Jan. 17, 2020 – present), and compiles a case-sensitive list of all of the unique word/contexts appearing within that interval. Essentially, it collapses all of the words appearing in a given context in that interval into a single row. Thus, all mentions of "impact" as a noun will be collapsed into a single row, while if "impact" also appears as a verb in that interval, its verb usage will appear as a second row. Characteristics such as aspect, case, form, gender, mood, number, person, properness, reciprocity, tense, voice and dependency label are all considered in this grouping, meaning if the word "impact" always appears as a verb in the given interval, but with different dependency labels, each use context will appear as a separate row.
For each unique word use context in a given interval, the system includes up to 5 examples of the word being used in that context, each of which includes a 5-word snippet of the usage and the URL it appeared in.
A single line of SQL is all that is required to search this 101-billion-record dataset to find all words that have appeared within 5 words of "climate change" OR "global warming" OR "climate crisis" OR "greenhouse gas" OR "greenhouse gases" OR "carbon tax" in these example snippets in English language coverage over the past four years. The final query can be seen below:
SELECT min(dateTime) dateTime, token, posTag, posMood, posNumber, posTense, dependencyLabel, example.context, example.url FROM `gdelt-bq.gdeltv2.web_pos`, unnest(examples) example WHERE lang='en' and (LOWER(example.context) like '%climate change%' OR LOWER(example.context) like '%global warming%' OR LOWER(example.context) like '%climate crisis%' OR LOWER(example.context) like '%greenhouse gas%' OR LOWER(example.context) like '%carbon tax%') group by token, posTag, posMood, posNumber, posTense, dependencyLabel, example.url, example.context order by dateTime desc
It is important to remember that example snippets are selected at random, meaning that within a given 15 minute interval, the system aggregates all mentions of "denies" as a verb and selects five examples of its use in that interval. Even if "denies" appears in the context of climate change as in "he again denies climate change", it might not be selected as one of the five example usages in that given 15 minute interval. The same snippet may appear multiple times if it was selected the example for multiple words that appear within it.
Thus, this dataset is highly incomplete and overlapping and includes just a fraction of the climate change mentions over this period since it was not designed for this purpose, but for those examples that do mention climate change, the end result is a rich linguistic look at the words appearing alongside it over time. In this case just a subset of characteristics were extracted, including the date/time the document was processed by the Natural Language API (which may not have been the time the article was first published but typically is), the token in question, the part of speech, mood, number, tense, dependency label, example snippet and URL it was drawn from.
In short, the Web Part of Speech Dataset is organized as a word/context-centric database, with example snippets selected at random and thus searching for word/contexts that contain climate change in their randomly selected example contexts yields only an imperfect subsample of mentions, but for those mentions it does return, the rich linguistic indicators allow powerful semantic and contextual filtering.
The final dataset is in CSV format and the image at the top of this page shows an example of its format.
We're excited to see how you might make use of this dataset!
- Download The Dataset. (154MB compressed / 1.1GB uncompressed).