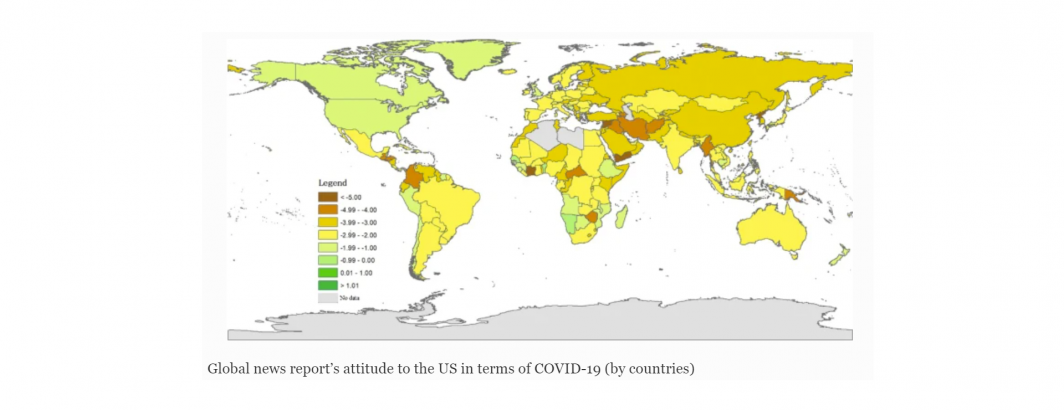
The outbreak of the coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has infected hundreds of millions of people worldwide and caused millions of deaths. This study used media analysis and correlation analysis to elucidate the significant differences in the ways in which news reports from 228 countries discussed a specific country when covering the COVID-19 pandemic. Media reports analysed in this study were collected from the Global Database of Events, Language, and Tone project (GDELT). These differences were found to be deeply embedded in the economic, socio-political, and cultural contexts of different countries. The findings reinforced the hypothetical assumption in framing theory and promoted a measurable and upscaled use of framing theory into macro geography studies. This study highlights the urgent need of a geo-political examination of COVID-19 in the global context—an area with insufficient interest from interdisciplinary perspective beyond epidemiology. Further research can be of great value for the promotion of an effective international cooperation mechanism to curb the spread of COVID-19.