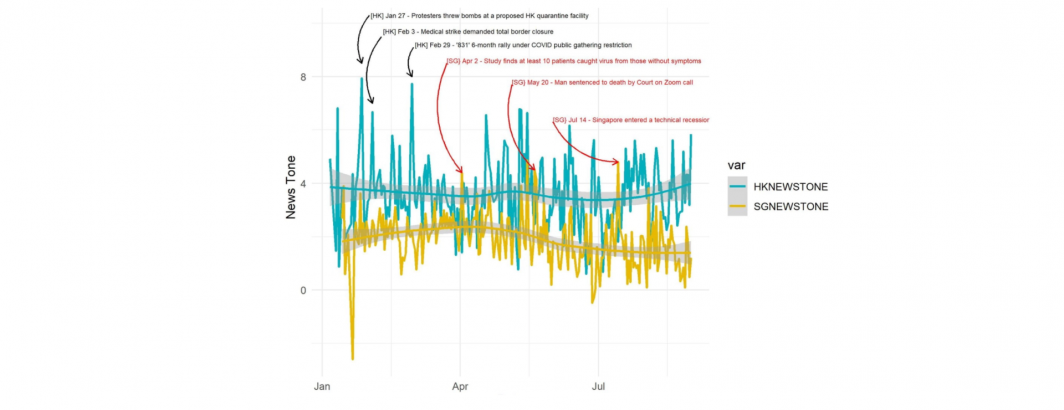
This fascinating study uses the GKG to explore how Singapore and Hong Kong responded to the Covid-19 pandemic:
The East Asian experience in tackling COVID-19 has been highly praised, but this high-level generalisation neglects variation in pandemic response measures adopted across countries as well as the socio-political factors that shaped them. This paper compares the early pandemic response in Singapore and Hong Kong, two Asian city-states of similar sizes, a shared history of SARS, and advanced medical systems. Although both were able to contain the virus, they did so using two very different approaches. Drawing upon data from a cross-national, probability sample Internet survey conducted in May 2020 as well as media and mobility data, we argue that the different approaches were the result of the relative strength of civil society vs. the state at the outset of the outbreak. In protest-ridden Hong Kong, low governmental trust bolstered civil society, which focused on self-mobilisation and community mutual-help. In Singapore, a state-led response model that marginalised civil society brought early success but failed to stem an outbreak among its segregated migrant population. Our findings show that an active civil society is pivotal to effective outbreak response and that trust in government may not have been as important as a factor in these contexts.